Rework: A short introduction
Besides ensuring traceability and recover value (instead of scrapping the WIP), it also helps to improve yield, customer deliveries and their quality requirements.
Can Rework be done indefinitely and without any control?
It’s why it may be necessary to restrict the number of times a lot can be reworked due to quality concerns, or even forbidding rework at all. Lots can often only tolerate a limited number of reworks before they become unusable and, in some cases, rework may not be permitted at certain process steps or for specific reasons.
CM MES now provides a mechanism to restrict the number of reworks for materials:
- Global Limit by Product: Apply an overall rework limit for a specific product.
- Limit by Step: Define rework limits at specific process steps using a Smart Table
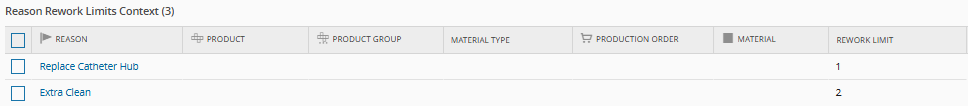
- Limit by Rework Reason: Restrict reworks based on the reason, using a Smart Table
- Combination of Limits: Apply these restrictions individually or in combination.
Taking the example above, the lithography process cannot be redone infinitely if misalignment continues to be found at the end of the process. Not to mention the cost of photoresist, labor, and the degradation of reticles, excessive rework can damage underlying layers, and it is better to reject a few misaligned or contaminated dies rather than scrap entire wafers.
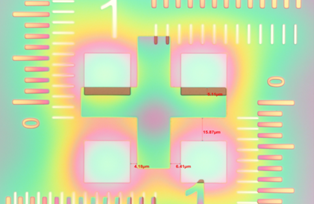
How MES manages rework limits
In medical industry some products cannot perform rework at all, while others may be reworked but with limits.
The following configurations were defined for this demonstration:
Product properties: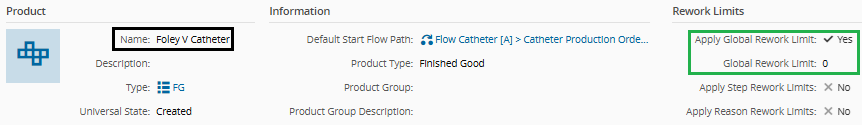
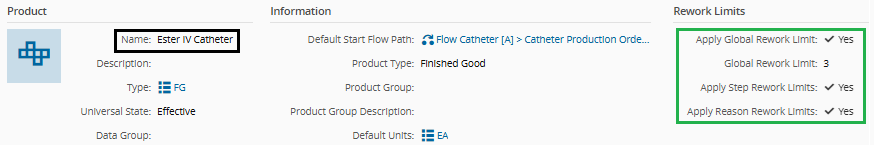
Context resolution table configuration: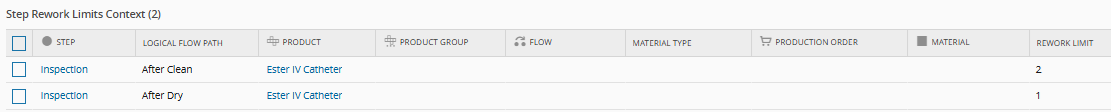
Here is a demo to show the configurations:
Rework features available in Critical Manufacturing MES
In addition to rework limits, these are the other available related features
Simple Design of Rework Flows
Create and manage rework flows with an intuitive and streamlined approach.Integration with Standard Process Steps
Associate rework operations directly with standard manufacturing steps to ensure full process alignment.Configurable Rework Reasons
Define multiple rework reasons, with the ability to link different rework flows to specific process steps.Flexible Return Points
Configure rework flows to return materials to any designated step within the process flow.State-Based Rework Application
Control when rework can be applied by defining eligible states: Queued, In Process, or both.Rule-Based Triggers
Automatically execute predefined rules when a material is sent for rework — from simple notifications to advanced actions, such as initiating a warehouse transfer request to supply critical Moisture-Sensitive Level (MSL) components required for the rework operation.Traceability and Data
All operations are recorded, and data are available for reports and KPIs.
Final thoughts
Author
I’ve been with Critical Manufacturing since 2018, starting out as an MES Consultant. Earlier this year, I stepped into the recently created Advocate & Architecture team. My role sits at the intersection of technology, communication, and strategy. Making sure solutions are technically sound and that everyone understands how to use or build them.
You can check me on LinkedIn
